Linen is a natural fabric derived from plant fibers, commonly utilized in the production of garments, drapes, table linens, cushions, carpets, ropes, and various other items. This textile is celebrated for its breathability, strength, and adaptability, though it can be susceptible to wrinkling and can feel stiff. To enhance its softness and reduce creasing, linen is frequently combined with cotton, another natural fiber from plants.
Contents
What is linen fabric?
Linen is a breathable and eco-friendly textile derived from the fibers of the flax plant. This plant, known scientifically as Linum usitatissimum, typically reaches a height of 3 to 4 feet. The taller varieties are used to produce fabric, while the seeds are processed to create linseed oil and flax milk.
The height of the flax plant directly correlates with the length of its fiber. This fiber is recognized as the strongest natural fiber globally, significantly surpassing the durability of cotton. Flax thrives in temperate regions, reaching maturity in about 100 days, and it flourishes in full sunlight with moist soil conditions.
Linen versus Cotton
Linen and cotton are comparable textiles, both originating from the fibers of distinct plants that share similar characteristics. Cotton, a natural fiber, is obtained from the fibers found in the fruit capsules, known as bolls, of the cotton plant. In contrast, linen is produced from the fibers harvested from the stems of the flax plant.
Linen is often two to three times stronger than cotton and has a quicker drying time, which aids in heat dissipation. However, it tends to be pricier and has less elasticity, resulting in more wrinkles compared to cotton.
The Evolution of Linen Textile
The flax plant has been grown in nearly every nation and has been utilized for fiber production for millennia. Archaeological findings suggest that humans have been using flax for over 35,000 years, tracing back to the Paleolithic era. In ancient Egypt, linen was highly valued and employed to wrap mummies, playing a significant role in the preservation of these historical artifacts.
The antibacterial and antifungal characteristics of linen have historically rendered it a vital fabric for use in combat zones. In contemporary times, linen is often combined with cotton to produce a robust, paper-like material utilized in the manufacturing of American currency. Flax is now cultivated globally, with significant production in Europe, Canada, China, India, and the United States.
What is the process of creating linen fabric?
Contemporary linen production closely resembles the methods used in ancient Egypt. The flax plants are manually harvested, either by cutting or pulling, with the latter technique often resulting in a finer quality of linen. After harvesting, the flax is left to dry for a few weeks. The next step involves threshing, which is the process of separating the seeds from the stalks. In certain instances, flax is collected before the seeds are fully developed to yield a more robust fiber.
Soaking or immersing the stalks of the flax plant aids in the extraction of intact fibers, with some of the longest fibers reaching almost 8 inches in length. These fibers are subsequently twisted into yarn and crafted into fabric.
Advantages and Applications of Linen
Linen is a favored textile option for a variety of reasons:
- Highly absorbent due to its porous structure and ability to wick away moisture, this fabric is a popular choice for summer apparel and bedding.
- Linen is an excellent heat conductorit holds heat within its fibers while allowing the skin to remain cool.
- Airy and Comfortable: This material promotes enhanced airflow around your body, resulting in linen garments that are light and pleasant to wear.
- Simple to color: The natural fibers of this fabric retain dye hues more effectively than other materials, resulting in a wide array of color options.
- Antibacterial and hypoallergenic properties: Linen possesses natural antibacterial and antifungal qualities, which is why it is often favored for use in bandages and bedding. Additionally, its hypoallergenic nature makes it an excellent option for individuals with allergies.
- Durable: This natural fabric boasts an impressive lifespan, exceeding that of cotton, and can endure for over 30 years.
- Environmentally friendly: This sustainable fabric decomposes rapidly, consumes less water compared to cotton during its cultivation, and thrives in difficult conditions, making it a planet-friendly option.
Varieties of Linen Textiles
Linen varieties can be identified by their texture, weaving style, and the method of their construction.
- Damask linen is a richly detailed and delicate type of linen fabric, crafted on specialized looms to mimic intricate embroidery. It is commonly utilized in various crafts and home decoration projects.
- Linen with a plain weave: This fabric, known for its somewhat coarse texture and durability, is commonly utilized for hand and bath towels.
- Lightly textured linen: This practical material is commonly utilized in washable diapers and for various crafting projects.
- Linen sheeting: This tightly woven material is frequently utilized in clothing and bed linens. It features a smooth, soft finish without any texture. Typically, the thread count is quite high, resulting in a robust and dense fabric.
- Linen blend: This material merges the finest attributes of cotton and linen, enhancing softness and comfort, and reducing the likelihood of wrinkles. Additionally, linen blends tend to be more affordable than 100% linen.
Linen Maintenance
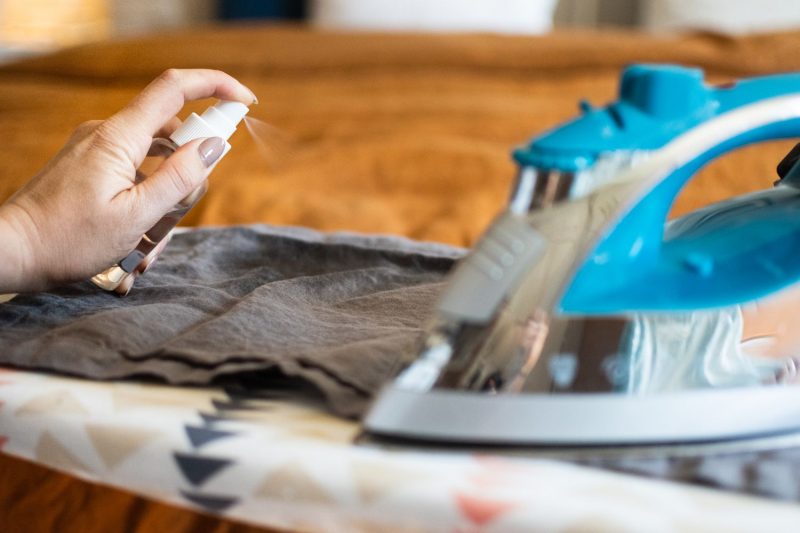
If you appreciate the aesthetic and texture of linen apparel, mastering the art of ironing linen can help you manage its well-known wrinkles, unless you favor a more relaxed, creased appearance. Utilizing a high temperature on your iron and applying a bit of spray starch, particularly on the collars, can produce a sleek and polished finish. Keep in mind that after wearing your linen piece, it will likely become somewhat wrinkled.
To minimize the appearance of wrinkles, choose fabrics that are a blend of linen. Ensure that your linen garments are thoroughly dry before putting them on, as wrinkles tend to become more pronounced when the fabric is wet.
What is Starch?
Laundry starch is a spray usually composed of water and cornstarch. This product enhances the texture and firmness of fabrics, provides protection against stains and pilling, minimizes static cling, and simplifies the ironing process.
This material becomes more supple with wear. To keep your linen garments looking fresh and durable, opt for dry cleaning. One of the advantages of linen is that it is machine washable, but, similar to cotton, it is prone to shrinking. When laundering linen, use cold or warm water. Exercise caution when treating stains, as some dyed linen fabrics may not hold their color. Always check a hidden area for colorfastness before proceeding.


What is the price of linen fabric?
Typically, the price of linen fabric ranges from a few dollars per yard for lower quality options to around $20 for those of superior quality. Organic linen tends to be the most expensive.
What are the ways to determine if a fabric is made entirely of linen?
The new fabric made entirely of linen is lightweight, features a somewhat coarse texture, creases easily, and has a cool sensation when touched.
Which is superior, pure linen or pure cotton?
When comparing pure linen and pure cotton, linen excels in terms of durability and breathability, while cotton offers a softer feel and is less prone to wrinkling. A blend of linen and cotton strikes the ideal balance, providing a combination of durability, softness, and reduced wrinkling.